Clipping range in Blender cameras determines how far and how close objects must be to remain visible within the camera’s view. If an object falls outside the defined clipping range, it will not appear in the rendered image or viewport. Understanding and adjusting the clipping range is essential for preventing rendering issues and optimizing scene performance.
Understanding Clipping Range
The clipping range consists of two values:
- Near Clipping: The minimum distance from the camera where objects become visible. Anything closer than this distance will be cut off.
- Far Clipping: The maximum distance from the camera where objects remain visible. Anything beyond this distance will be invisible to the camera.
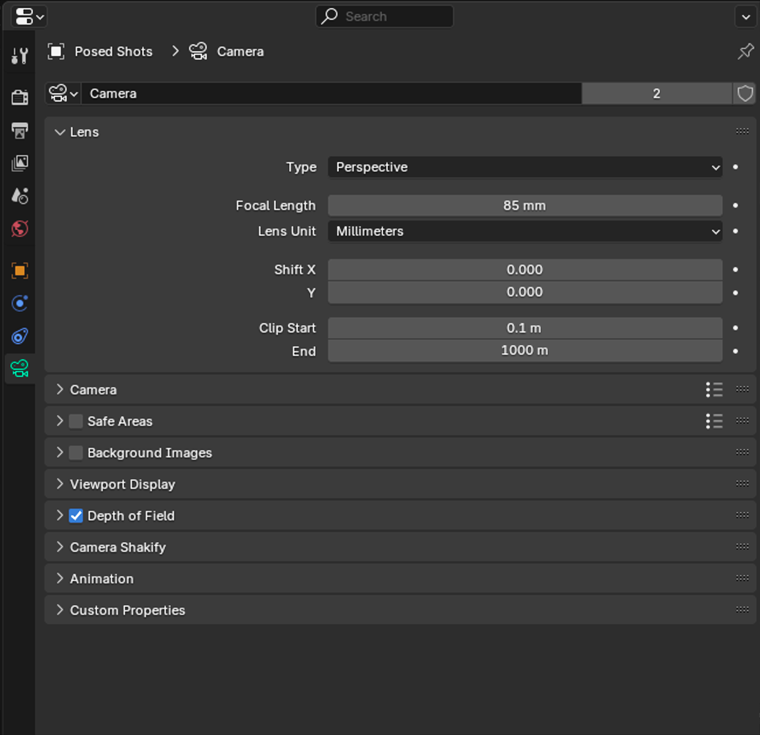
By default, Blender sets the near clipping to 0.1m and the far clipping to 1000m, but these values can be adjusted depending on the needs of your scene.
How to Adjust the Clipping Range in Blender
1. Access Camera Properties
- Select the camera in your scene.
- Navigate to the Camera Properties tab (camera icon).
2. Modify Clipping Values
- Locate the Clipping Start and Clipping End fields.
- Adjust the Start value to set the near clipping distance.
- Adjust the End value to set the far clipping distance.
Why Adjust the Clipping Range?
1. Fixing Clipping Issues in the Viewport
- If objects appear cut off when zooming in or out, increasing the near clipping value can help resolve the issue.
2. Improving Performance
- Lowering the Far Clipping value can help optimize performance, especially in large scenes with distant objects.
3. Ensuring Correct Rendering
- Objects disappearing in renders may be due to incorrect clipping values. Adjusting them ensures all necessary elements appear correctly.
Clipping Range in Different Camera Types
Blender’s clipping range settings apply to all types of cameras, including:
- Perspective Cameras: Standard cameras used for realistic depth.
- Orthographic Cameras: Used for technical and blueprint-like renders where clipping controls how much of the scene remains visible.
- Panoramic Cameras: Essential for 360-degree and VR renders, where incorrect clipping values can cause elements to disappear.
Using The View Keeper to Manage Clipping Settings
If you work with multiple cameras in a scene, you could have need for cameras with different clipping ranges. The View Keeper simplifies this by allowing users to store and switch between camera setups, including different clipping ranges. This is especially useful for scenes requiring both extreme close-ups and vast environmental shots.
How The View Keeper Helps:
- Store different clipping settings per record.
- Quickly switch between cameras with different clipping values.
- Batch render multiple camera views with preset clipping settings.
For example, in an architectural visualization, you may need one camera shot with a small near clipping value for close-up details and another with a large far clipping value to capture a full building view. The View Keeper allows seamless switching between these setups with the click of a button.
Tips for Setting Clipping Ranges
- Avoid setting the near clipping too low (below 0.01m), as it can cause depth artifacts.
- Adjust the far clipping based on the scene size. Using extreme values (e.g., over 10,000m) can cause performance issues for large or complex scenes.
- Check clipping values before rendering to ensure important objects are not cut off.
- Use The View Keeper to store and manage different clipping ranges for different shots using one camera.
Common Issues with Clipping Range
Why are objects disappearing when I zoom in?
- Your Near Clipping value might be too high. Lower it to make objects visible at close range.
Why are distant objects missing in my render?
- The Far Clipping value may be too low. Increase it to extend visibility.
Does the clipping range affect render times?
- Yes. A high Far Clipping value in complex scenes can slow down rendering. Adjust it according to scene requirements.
Can I set different clipping values for different cameras?
- Yes, using The View Keeper, you can store and manage different clipping settings for each camera in your scene. It can also let you store and manage different clipping range on one camera.
How do I reset clipping values to default?
- Simply set the Start value to 0.1m and the End value to 1000m in the Camera Properties panel.
Why does my scene look empty when I move the camera?
- Your near clipping value might be too high, preventing objects from appearing.
Can clipping values affect reflections or shadows?
- Yes, extremely high or low clipping values can cause shadow or reflection artifacts, especially in Cycles.
The clipping range in Blender cameras is a fundamental setting that directly affects how objects appear in both the viewport and final renders. Proper management of near and far clipping values ensures a smooth workflow, prevents visual errors, and optimizes performance. Tools like The View Keeper further enhance camera management by allowing users to store and switch between multiple configurations on the same or multiple camera, including clipping settings, effortlessly. By mastering clipping range settings, you can achieve better control over your Blender scenes and renders.