Motion blur is an essential technique in filmmaking and animation, adding a sense of speed, realism, and fluidity to moving objects and cameras. In Blender, motion blur can be applied to camera movement, helping to create cinematic effects, enhance storytelling, and mimic the imperfections found in real-world photography and film.
Blender offers multiple ways to achieve motion blur, depending on the rendering engine you are using. Understanding how motion blur works and how to control it effectively ensures that your final renders look dynamic and professional.
Understanding Motion Blur in Blender
Motion blur occurs when an object moves rapidly during the exposure time of a camera, causing streaks or smearing in the final image. In traditional photography and film, motion blur is a natural result of slower shutter speeds capturing movement over time. In 3D rendering, motion blur must be simulated artificially, and Blender provides built-in tools to achieve this effect.
Blender’s motion blur settings primarily affect:
- Camera movement (such as panning, tilting, or dolly motion)
- Object movement (individual objects moving within a scene)
- Deformation motion (objects changing shape or form dynamically)
For camera motion blur, Blender calculates how much the camera moves between frames and applies blur accordingly. This effect is especially useful in action shots, fast camera pans, or chase sequences, where motion blur enhances the feeling of movement and speed.
When to Use Motion Blur
Motion blur is not always necessary, but when used correctly, it can greatly enhance an animation or still render. Here are some scenarios where motion blur is particularly useful:
- Action Scenes: Fast-paced action sequences benefit from motion blur as it conveys speed and movement effectively. This is especially useful in chase scenes, explosions, or dynamic fight sequences.
- Camera Movements: When the camera is panning, tilting, or performing a rapid dolly move, motion blur prevents the animation from looking too rigid or artificial.
- First-Person Perspective Shots: In animations that simulate first-person movement, such as walking or running sequences, motion blur makes transitions feel more natural and less jarring.
- Vehicle or Object Motion: Moving objects such as cars, planes, or characters running at high speed can appear more dynamic with motion blur applied.
- Cinematic Effects: If you are aiming for a film-like appearance, motion blur can add realism by mimicking the natural imperfections of real-world cameras.
- Game Cutscenes and Pre-Rendered Animation: Motion blur can be used in pre-rendered scenes to make animations appear more polished and fluid, particularly in high-speed sequences.
However, motion blur may not always be ideal. If your scene requires a crisp, sharp look such as in technical animations, architectural visualizations, or product renders. In cases like these, reducing or disabling motion blur is recommended.
Enabling Motion Blur in Blender
Blender makes it easy to add motion blur through its Render Properties panel. The steps vary slightly depending on the rendering engine being used.
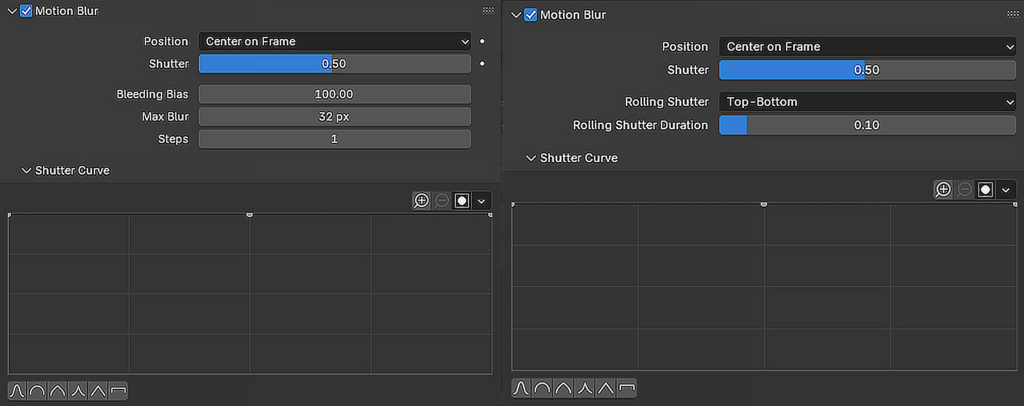
1. Enabling Motion Blur in Cycles
Cycles, Blender’s physically accurate path-tracing engine, offers built-in motion blur that closely mimics real-world photography.
- Open Render Properties.
- Locate the Motion Blur section and enable it.
- Adjust the settings:
- Position
- Shutter
- Rolling Shutter
- Rolling Shutter Duration
- Shutter Curve
2. Enabling Motion Blur in Eevee
Eevee, Blender’s real-time rendering engine, also supports motion blur, but it functions differently from Cycles.
- Open Render Properties and enable Motion Blur.
- Adjust the following parameters:
- Position
- Shutter
- Bleeding Bias
- Max Blur
- Steps
- Shutter Curve
Eevee’s motion blur is screen-space based, meaning it doesn’t simulate true 3D motion blur as Cycles does, but it is highly efficient for real-time previews and game cinematics.
Fine-Tuning Motion Blur for Better Results
Once motion blur is enabled, fine-tuning the settings is crucial to achieving the right effect for your scene. Too much blur can make a scene look messy, while too little might not convey the intended speed or motion impact.
1. Adjusting Shutter Speed for Realism
Shutter speed setting plays a major role in how motion blur appears in Blender. The Shutter setting determines how long a frame’s exposure lasts, similar to real-world cameras.
- Lower shutter values (0.1 – 0.3) create minimal blur, useful for subtle motion effects.
- Medium shutter values (0.4 – 0.6) produce natural-looking blur for moderate movement.
- Higher shutter values (0.7 – 1.0) generate strong blur effects, great for fast-moving shots.
For cinematic effects, a value between 0.5 and 0.7 usually provides the best balance of motion and clarity.
2. Controlling Object Motion Blur
While motion blur is typically applied to moving cameras, objects in the scene also contribute to the effect. If an object moves rapidly across the frame, Blender can simulate motion streaks using object-based motion blur settings.
- Ensure Motion Blur is enabled in the Render Properties.
- Select the moving object and go to Object Properties.
- Under Motion Blur, adjust the Steps parameter (EVEE). Higher values provide smoother blur trails.
- Experiment with different motion speeds to see how the effect reacts in animation.
3. Using Vector Pass for Post-Processing Control
Blender allows users to tweak motion blur even after rendering by enabling the Vector Pass in the View Layer Properties.
- Enable Vector Pass in the View Layer Properties.
- Render the scene and switch to the Compositor.
- Use the Vector Blur node to fine-tune blur effects in post-production.
This method is particularly useful for adjusting motion blur without having to re-render frames, saving valuable time in long animation sequences.
Combining Motion Blur with Depth of Field
Motion blur and depth of field (DoF) are two powerful cinematic effects that, when used together, can greatly enhance the realism and visual appeal of an animation. Motion blur simulates the streaking effect caused by movement, while depth of field controls how much of the scene remains in focus.
1. Why Combine Motion Blur with Depth of Field?
- Increases Realism: Real-world cameras naturally exhibit both effects simultaneously, and combining them in Blender makes renders look more lifelike.
- Directs Viewer Focus: A strong DoF effect can keep the audience’s attention on key elements while motion blur enhances movement.
- Enhances Cinematic Quality: Combining motion blur and DoF replicates techniques used in Hollywood films, adding a professional touch to animations.
2. How to Enable Depth of Field Alongside Motion Blur
- Select the Camera in the Outliner or 3D view.
- In the Camera Properties panel, locate the Depth of Field section.
- Choose an object to focus on or manually set the Focus Distance.
- Adjust the F-Stop value to control the amount of blur (lower values create stronger DoF effects).
- Ensure Motion Blur is enabled in the Render Properties.
3. Balancing Both Effects for the Best Results
- Avoid excessive blur: Too much motion blur combined with a strong depth of field can make the scene unreadable.
- Test different shutter speeds: Adjusting the Shutter value in Motion Blur settings helps find the right balance.
- Use the Viewport Preview: Eevee’s real-time rendering can help visualize both effects before final rendering.
Using The View Keeper for Depth of Field Management
While The View Keeper doesn’t currently store motion blur settings, it does store depth of field settings. This allows you to experiment with different camera setups without the need to duplicate cameras or manually switch settings.
How The View Keeper Helps with Depth of Field:
- Store multiple camera settings, including different depth of field intensities.
- Switch between different depth of field setups instantly with a single click.
- Use Alternative Rendering to render multiple depth of field variations at once, reducing manual work.
For example, in an action sequence, you might need varying depth of field levels combined with motion blur. With The View Keeper, you can set up different camera configurations and quickly switch between them with a single click manually or through keyframing for animation.

Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting Motion Blur
Why is my motion blur too extreme or too weak?
Adjust the Shutter value in the Motion Blur settings. A lower value reduces blur, while a higher value increases it. Experiment with values between 0.4 and 0.7 for natural results.
Why does my motion blur look unnatural in Eevee?
Eevee’s motion blur is screen-space based, meaning it may not match real-world motion blur. Try tweaking the Max Blur and Shutter Position settings for better results.
Why is my scene clipping when I apply motion blur?
If objects disappear or clip when motion blur is applied, increase the Clip Start and Clip End values in the Camera Properties to avoid rendering cutoffs.
How do I improve the smoothness of motion blur in fast-moving objects?
Increase the Max Steps value in the Motion Blur Settings under Render Properties. This helps capture motion trails more accurately.
Why does my motion blur create strange artifacts?
Artifacts can result from insufficient samples in Cycles or overlapping motion in Eevee. Increasing Sample Rate in Cycles or adjusting the Shutter Position in Eevee can help reduce artifacts.
Can I add motion blur to existing renders?
Yes! You can add motion blur to existing renders using the Vector Pass and the Vector Blur node in Blender’s Compositor. However, for this to work correctly, you must ensure that the Vector Pass is enabled in the Render Layer properties before rendering.
How do I keyframe motion blur settings?
Motion blur settings in Blender cannot be keyframed directly, as they are part of the Render Properties, which do not support keyframing. However, you can animate motion blur effects by Animating the Shutter Speed
Why is my render time increasing significantly with motion blur?
Motion blur requires additional calculations per frame. In Cycles, reducing the number of motion blur steps or lowering sample counts can help balance performance and quality.
Motion blur is an essential tool in Blender for achieving natural, cinematic visuals. Whether applied through Cycles for photorealism or Eevee for real-time effects, understanding how to fine-tune motion blur ensures your renders feel dynamic and lifelike.
While motion blur enhances movement, depth of field helps improve this by direcing focus. The two often work together for a more immersive result. Working with Blender’s default settings can be restrictive, often requiring you to commit to a particular configuration with no built-in way to expreiment between different setups. This makes experimenting with motion blur settings, depth of field, and various camera parameters frustrating, especially when working on complex scenes. The View Keeper removes these limitations.
With The View Keeper, you can freely test what your motion blur looks like with different depth of field values, camera angles and more without worrying about losing previous settings. If one setup doesn’t work, you can instantly switch back to a previous one or compare between different versions something that Blender alone doesn’t allow. Instead of manually adjusting settings for every test render, you can save, recall, and refine your choices with a single click.
This flexibility gives you more creative control over motion blur, letting you focus on perfecting your visuals rather than struggling with repetitive adjustments. Whether you’re crafting fast-paced action shots or subtle cinematic scenes, The View Keeper ensures you always have the best version of your work at your fingertips.