The “Follow Path” constraint is a powerful tool in Blender. It is a tool that makes your camera move along a curve. This is simply giving your camera a predefined path to follow. In this article, we will learn what the Follow Path constraint is, how it works, and why it is important. We will also see examples to help you understand its power.
A Simple Way to Move Your Camera
Imagine you are on a roller coaster. The track guides your car along a smooth path as you move up and down on the roller coaster. In Blender, the Follow Path constraint works just like that track. It tells the camera where to go. The camera moves along a curve that you have created. This helps to show your scene in a very planned and organized way.
When you use this constraint, you do not need to keyframe every little move. Instead, you create a curve, add the camera, and tell it to follow the curve. This method saves time and makes your animation smooth. It is a favorite tool for many artists who work in Blender.
Why Use the Follow Path Constraint?
There are many reasons to use the Follow Path constraint. Here are a few important ones:
- Smooth Movement: It helps your camera move in a smooth and predictable way. Just like a train following its tracks.
- Cinematic Effects: Many movies use smooth camera moves. For example, in films like Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes, the camera glides through the scene following a specific path. The Follow Path constraint can create this same effect in Blender.
- Easy Control: Once you set up the path, you can easily adjust the speed and timing. This lets you focus on the story you want to tell.
- Creative Storytelling: In video games like Journey, smooth camera movement is key to the player experience. The Follow Path constraint helps bring this level of expereince and quality to your animations.
- Precision: For technical animations or architectural visualizations, it is important that the camera follows a precise path. This constraint makes sure the camera stays on course.
How to Set Up the Follow Path Constraint
Let us go through the steps to set up the Follow Path constraint for a camera in Blender.
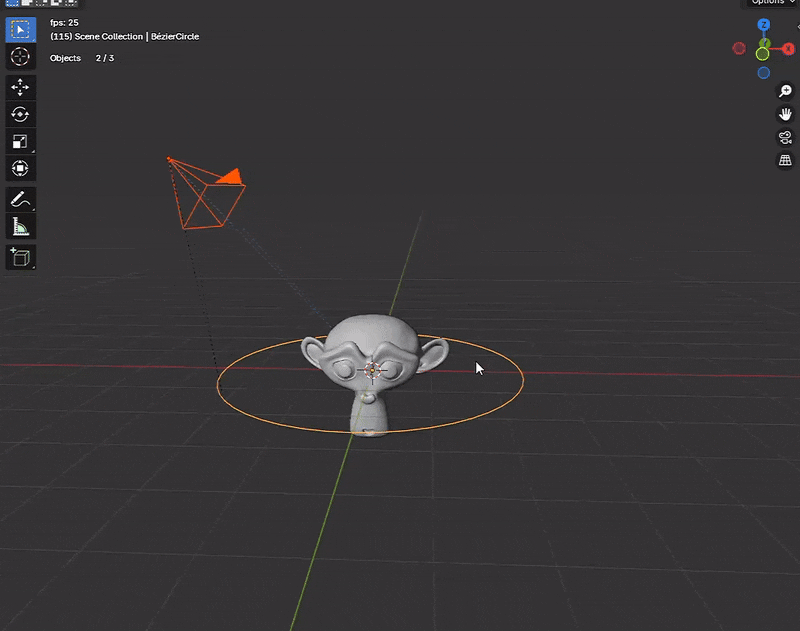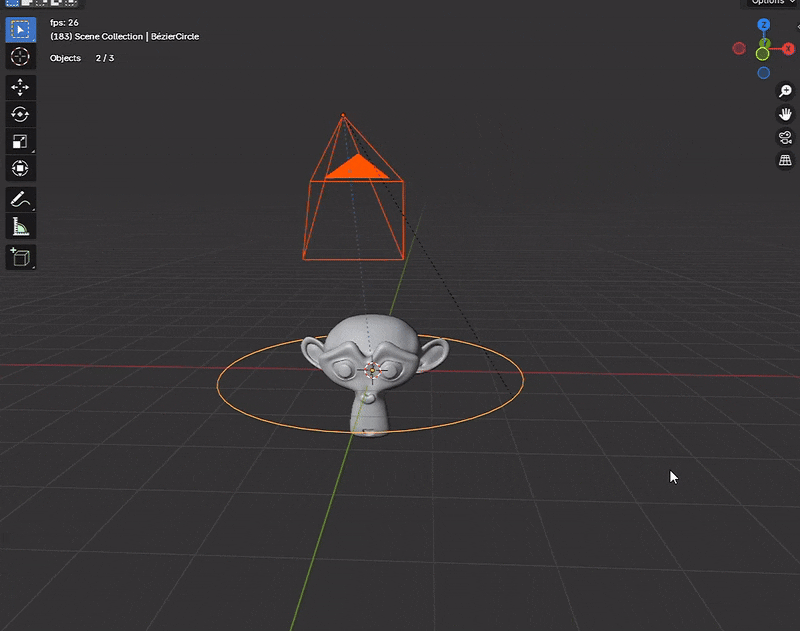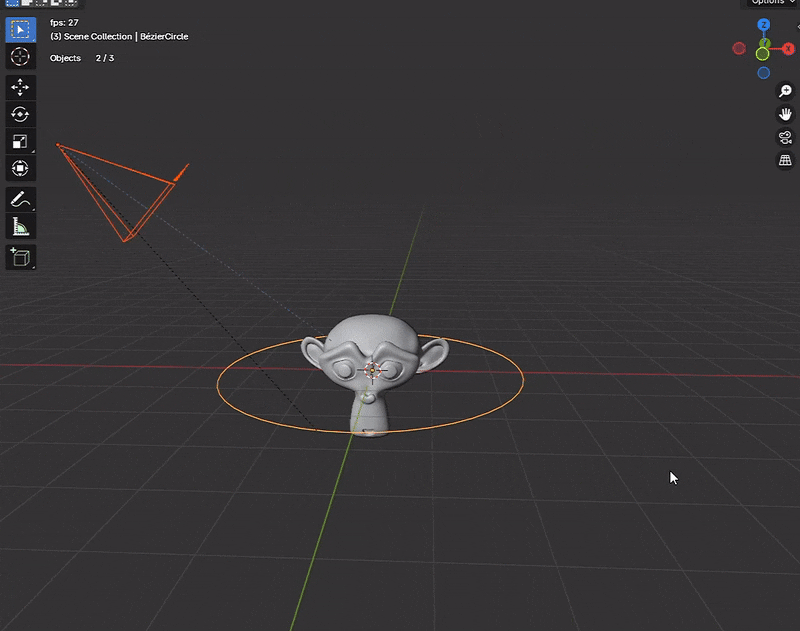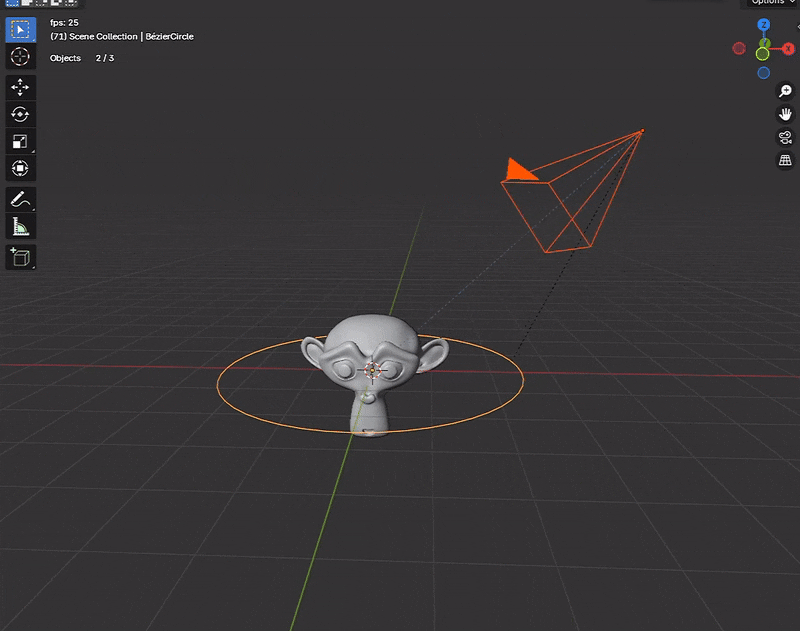
Step 1: Create a Path
First, you need to create a curve that the camera will follow. In Blender, you do this by:
- Pressing Shift + A to open the Add menu.
- Selecting Curve, then choosing Path or Bezier.
- Adjusting the shape of the curve in the 3D Viewport.
Think of this curve as a road for your camera. You can use the handles on a Bezier curve to change its shape. A smooth curve gives your camera smooth movement.
Step 2: Add a Camera
If you do not have a camera in your scene:
- Press Shift + A and choose Camera.
- Place the camera near the start of your curve.
You can move the camera by pressing G and rotate it with R. The camera should be positioned so that it is ready to follow the path.
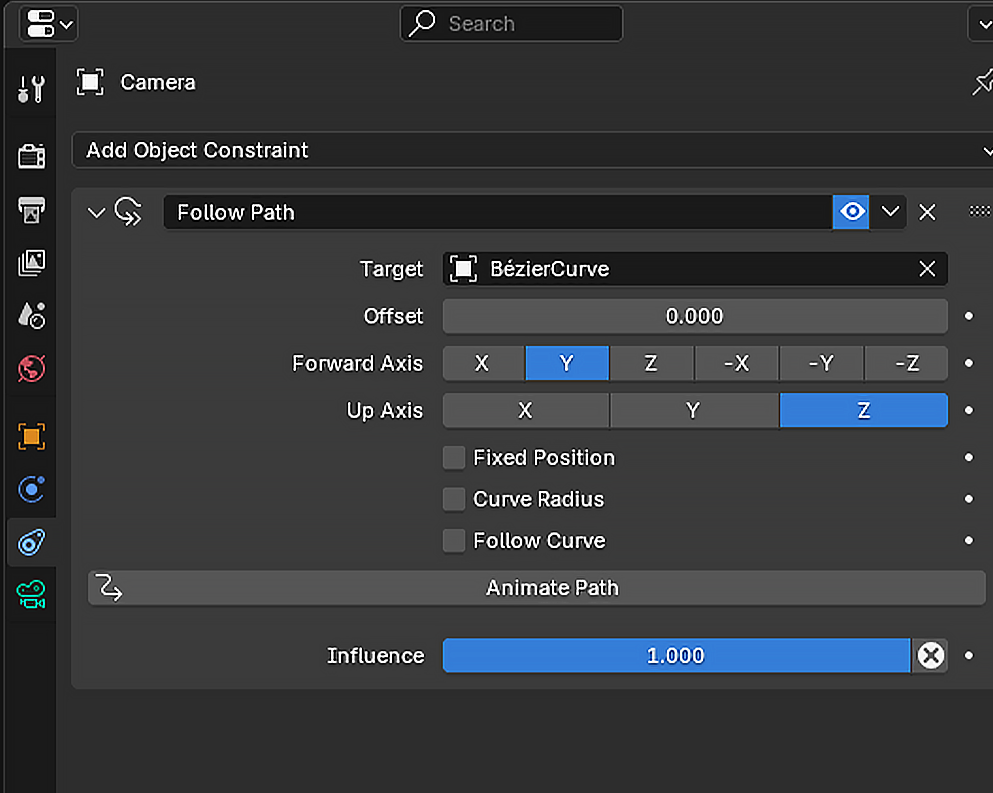
Step 3: Apply the Follow Path Constraint
Now, it is time to tell the camera to follow the curve.
- Select your camera.
- Go to the Constraints tab in the Properties Editor. This tab looks like a chain icon.
- Click Add Object Constraint and choose Follow Path.
- In the constraint settings, find the Target field. Click it and choose your curve.
This tells Blender which path the camera should follow.
Step 4: Animate the Camera Along the Path
After setting the constraint, you want your camera to move along the curve.
- With the camera still selected, click on the Follow Path constraint.
- You will see a button called Animate Path. Click it.
Blender will now add keyframes that make the camera travel along the curve over time. - You can adjust the timing by changing the Evaluation Time value in the curve’s data properties.
This value tells Blender how fast the camera moves along the path.
Step 5: Test the Animation
Press Spacebar or click the Play button in the Timeline to see your camera move. The camera should glide along the curve, following its shape closely. If the movement is too fast or too slow, adjust the keyframes or Evaluation Time accordingly.
Tips for Using the Follow Path Constraint
Here are some tips and tricks to help you make the most of the Follow Path constraint:
Use Clear and Simple Paths
The smoother and simpler your curve, the easier it is for your camera to follow. Complex curves can lead to unexpected movements. Start with a basic path and then refine it as needed.
Adjust the Speed
The speed of the camera can be controlled by changing the Evaluation Time on the curve. If your camera needs to move slowly to capture details, increase the spaces between keyframe. For a fast-paced scene, shorten the time between keyframes. This is similar to controlling the pace in a movie.
Combine with Other Constraints
Sometimes, you might want your camera not only to follow a path but also to look at a specific object. In this case, you can add a Track To constraint along with the Follow Path constraint. The Track To constraint will ensure that the camera always faces the object. For example, if you are filming a moving car, you can make the camera follow a curved path while always keeping the car in view.
Experiment with Different Paths
Try different types of curves such as Bezier or NURBS. Each type gives a different feel to the camera movement. A Bezier curve might offer smoother transitions, while a NURBS curve can create more precise paths. Experimentation helps you find the best path for your scene.
Use The View Keeper
The View Keeper is a crutial tool in cases where you have multiple camera setups. Using The View Keeper in Blender, you can save multiple camera setups that include the Follow Path constraint. This tool allows you to quickly switch between different camera paths.
For example, in a car chase scene, you could have one camera that follows the car to capture the chase and another inside the car to capture the characters’ actions. You can even set up an additional camera for a second car chasing the first. With The View Keeper, switching between these camera setups is just a click away, and when you’re ready to render, it can render all shots in one session. If you want to save each shot to different folders and in different file formats, The View Keeper also makes that and so much more possible.
Real-World Examples and Inspirations
The concept of the Follow Path constraint is used in so many creative fields. Here are some examples to show its power.
Film and Television
Many films use smooth camera moves to create dramatic effects. In The Shining, for instance, the camera glides through the empty corridors to build suspense. The Follow Path constraint in Blender creates similar eerie, smooth transitions in your animations. This technique is also seen in movies like Gravity, where the camera follows the astronauts through space, giving a sense of weightlessness and calm.
Video Games
In video games, smooth camera movement is crucial for immersive cutscenes. Games like Uncharted and Tomb Raider use complex camera paths to follow the action and keep the player engaged. By using the Follow Path constraint, you can animate your camera to follow a character or move through a game level with precision. This makes your scenes feel more cinematic and polished.
Architectural Visualization
When creating architectural walkthroughs, a smooth camera path can show off the interior and exterior of a building in a clear and organized manner. The Follow Path constraint allows you to plan a guided tour of a virtual building. This is how architects present a 3D model design to clients, ensuring that every angle is explored and appreciated.
Art and Animation
Many animated shorts and experimental films use camera paths to add fluidity and grace to their scenes. For example, an animated music video might have the camera smoothly follow a character dancing through a dream-like landscape. The Follow Path constraint achieves this effect by ensuring that the camera moves in a consistent and deliberate manner. It is a favorite tool among artists who want to create visually engaging narratives.
Graphic Design and Virtual Tours
In graphic design, the concept of a camera following a path can be used to create dynamic presentations of products for marketing purposes. Virtual tours of museums or historical sites often rely on smooth camera transitions to give viewers a full experience of the space. By using the Follow Path constraint, you can create immersive visual content that draws viewers into the scene.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Even with a simple setup, you may face a few issues when using the Follow Path constraint. Here are some common problems and tips on how to solve them:
- The Camera Does Not Move:
Make sure you have clicked the Animate Path button. Check that your curve has keyframes set for Evaluation Time. - Unwanted Camera Rotations:
If the camera rotates unexpectedly, consider adding a Track To or Locked Track constraint to control its orientation. Adjust the “To” and “Up” axis settings to find the best configuration. - Camera Speed Is Off:
Adjust the Evaluation Time of your curve or change the keyframe timing to get the desired speed. Look at the Timeline to see how long it takes for the camera to travel the path. - The Path Is Not Smooth:
If your camera movement feels jerky, try smoothing out the curve. Use the handles on a Bezier curve to create a gentle flow. A smoother curve results in smoother camera motion. - Constraint Conflicts:
If you have more than one constraint on the camera, they might conflict. Disable other constraints one at a time to see which one is causing issues.
People Also Ask
- What is the Follow Path constraint in Blender?
The Follow Path constraint makes a camera move along a curve, guiding its motion in a smooth and controlled way. - How do I add a Follow Path constraint to a camera?
Select the camera, go to the Constraints tab, click “Add Object Constraint,” choose “Follow Path,” and set your curve as the target. - Can I adjust the speed of the camera on a path?
Yes, you can adjust the speed by changing the Evaluation Time in the curve’s properties or by editing keyframe timing. - What types of curves can I use with the Follow Path constraint?
You can use paths such as Bezier, NURBS, or any other curve type in Blender. - How do I make the camera face a target while following a path?
You can add a Track To or Locked Track constraint along with the Follow Path constraint to make the camera always face a specific object. - Can I animate the camera using the Follow Path constraint?
Yes, the Follow Path constraint is commonly used to animate camera movement in cinematic sequences and virtual tours. - What is the benefit of using a curve for camera movement?
Using a curve helps you plan smooth and precise camera paths. It makes the movement predictable and easy to adjust. - How do I smooth out a jerky camera movement?
Adjust the shape of the curve and refine the keyframe timings to create a smoother transition. - Is the Follow Path constraint useful for architectural visualization?
Yes, it is very useful for creating guided tours of virtual buildings and for showing every detail of a design. - Can I use the Follow Path constraint with multiple cameras?
Yes, you can set up the Follow Path constraint for each camera in your scene and switch between them as needed.
Bringing It All Together
The Follow Path constraint is a powerful tool in Blender that helps you create smooth, controlled camera movements. By using this constraint, you can set your camera to travel along a path with ease. Whether you are working on an animated film, a virtual tour, a game cinematic, or an architectural visualization, this tool offers great flexibility and control.
The process begins with creating a curve that serves as the path for your camera. Once the curve is in place, you add your camera and apply the Follow Path constraint. With a few simple steps, you can have your camera gliding through your scene like a smooth, moving train on its tracks. You can even combine this constraint with others, such as the Track To or Locked Track constraints, to ensure your camera always faces a key object.
This method is not only efficient but also opens up creative possibilities. Many filmmakers, game designers, and digital artists use camera paths to add a cinematic feel to their work. For instance, in many modern video games, the camera follows the player through a carefully planned path, creating an immersive experience. In films, smooth camera movements help build tension and focus the viewer’s attention. The Follow Path constraint in Blender allows you to bring these ideas to life in your own projects.
Advanced users can further refine their camera movements by experimenting with different types of curves using The View Keeper and adjusting keyframe timings. The speed and smoothness of the camera movement can be tailored to match the mood of your scene. For example, a slow, graceful movement might work best for a quiet, emotional scene, while a fast, dynamic move might be perfect for an action sequence.
The integration of tools like The View Keeper can help you save and manage different camera setups including those with the Follow Path constraint. With The View Keeper, you can store multiple camera records and easily switch between them, ensuring that your workflow remains efficient and accurate as you focus on your creative ideas.
As you continue to explore the Follow Path constraint, remember that practice is key. The more you work with this tool, the more natural it will become to set up complex camera movements. Experiment with different curves using The View Keeper, try combining constraints, and watch how your camera transforms your scene. Every project is an opportunity to learn and improve.
Final Thoughts
The Follow Path constraint for cameras in Blender is an essential tool for any artist looking to create smooth, dynamic animations and visualizations. It allows your camera to move along a predefined path with ease, much like a car driving on a set road. This not only saves time but also brings a level of professionalism to your work that is seen in high-quality films, video games, and architectural designs.
Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional, understanding and using the Follow Path constraint will open up new creative possibilities in your projects. It simplifies complex camera movements and helps you tell your story in a clear and engaging way.
Thank you for reading this article on what the Follow Path constraint is for cameras in Blender. We hope that these clear instructions, practical tips, and real-world examples have inspired you to try this technique in your own work. Enjoy exploring Blender, and may your camera paths guide you to many creative adventures.